Fixed Yield in DeFi Yield Farming Rewards
Fixed yield offerings in Decentralized Finance (DeFi) provide clear advantages over traditional finance (TradFi). They’re changing how people use financial services.
Enhanced Accessibility and Financial Inclusion: DeFi platforms don’t have the strict barriers common in TradFi. There’s no extensive paperwork or high minimum deposits. Anyone with an internet connection and a digital wallet can access these services worldwide. This promotes huge financial inclusion.
As of early 2025, over 15 million unique addresses have interacted with DeFi protocols. This is a 120% increase from 2022. It shows a growing global user base. It also highlights access for underserved populations.
For more: A Comprehensive Analysis of Yield and Payment Stablecoins
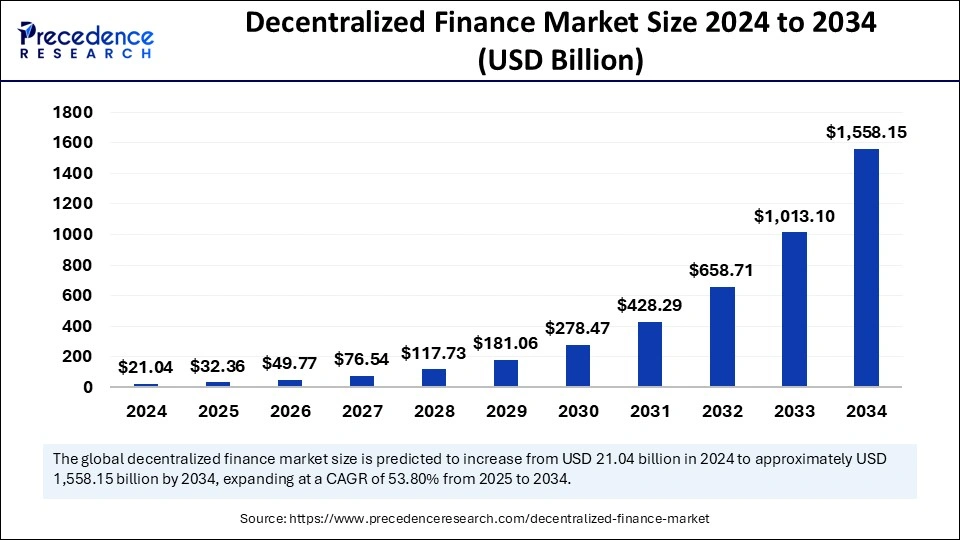

DeFi market size to hit $1558B in 2034
Unparalleled Transparency: A cornerstone of DeFi is its inherent transparency. All transactions are recorded on a public, immutable blockchain ledger, allowing users to track and verify their funds and protocol activities in real-time.
This contrasts sharply with the often opaque “behind-the-scenes” operations of traditional financial institutions. This public verifiability reduces hidden fees and enhances accountability, building trust among users.
Superior Efficiency and Lower Costs: By cutting out intermediaries like banks, brokers, and clearing houses, DeFi transactions are significantly faster and potentially cheaper. For instance, the cost of remittances through traditional channels averages 6.5% of the transfer amount, while DeFi platforms can reduce this to less than 1%, making international money transfers more accessible.
Additionally, settlement times for international transactions have been reduced from an average of 3-5 banking days to less than 5 minutes in 86% of DeFi transactions, an improvement of approximately 99.8%. This direct, peer-to-peer model reduces operational overheads, translating into higher profit margins for participants.
Empowered Self-Custody and User Control: In DeFi, users maintain direct control over their digital assets through their private keys, interacting directly with smart contracts. This eliminates the need to entrust funds to a central authority, fundamentally mitigating counterparty risk and empowering users with greater autonomy over their finances. This contrasts with traditional banking, where users rely on institutions to manage their funds.
Accelerated Innovation and New Product Development: DeFi is a rapidly evolving sector, constantly innovating with new protocols and financial products that push the boundaries of traditional finance.
The modular nature of DeFi, often called “money legos,” allows for the seamless integration and composability of different protocols. This fosters continuous development of novel yield-generating strategies and structured products. For example, the total number of DeFi DApps listed by Alchemy in 2025 stands at 354, with continuous development leading to new financial primitives and services not feasible in conventional systems.
Limitations and Risks Compared to Traditional Fixed Income
Despite its compelling advantages, fixed yield in Decentralized Finance (DeFi) carries inherent limitations and risks, generally less prevalent or managed differently in traditional fixed income. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for informed investment decisions.
For more: The Rise of Stablecoins: 2025 Market Update and Key Statistics
Higher Inherent Risk: DeFi investments, even with fixed rates, face greater fundamental risks than traditional bonds. These include smart contract vulnerabilities, which led to over $2.2 billion stolen in crypto-related hacks in 2024.
There’s also the potential for impermanent loss in liquidity pools and the inherent volatility of crypto assets; for example, Bitcoin and Ethereum show significantly higher volatility than traditional assets, impacting principal value.
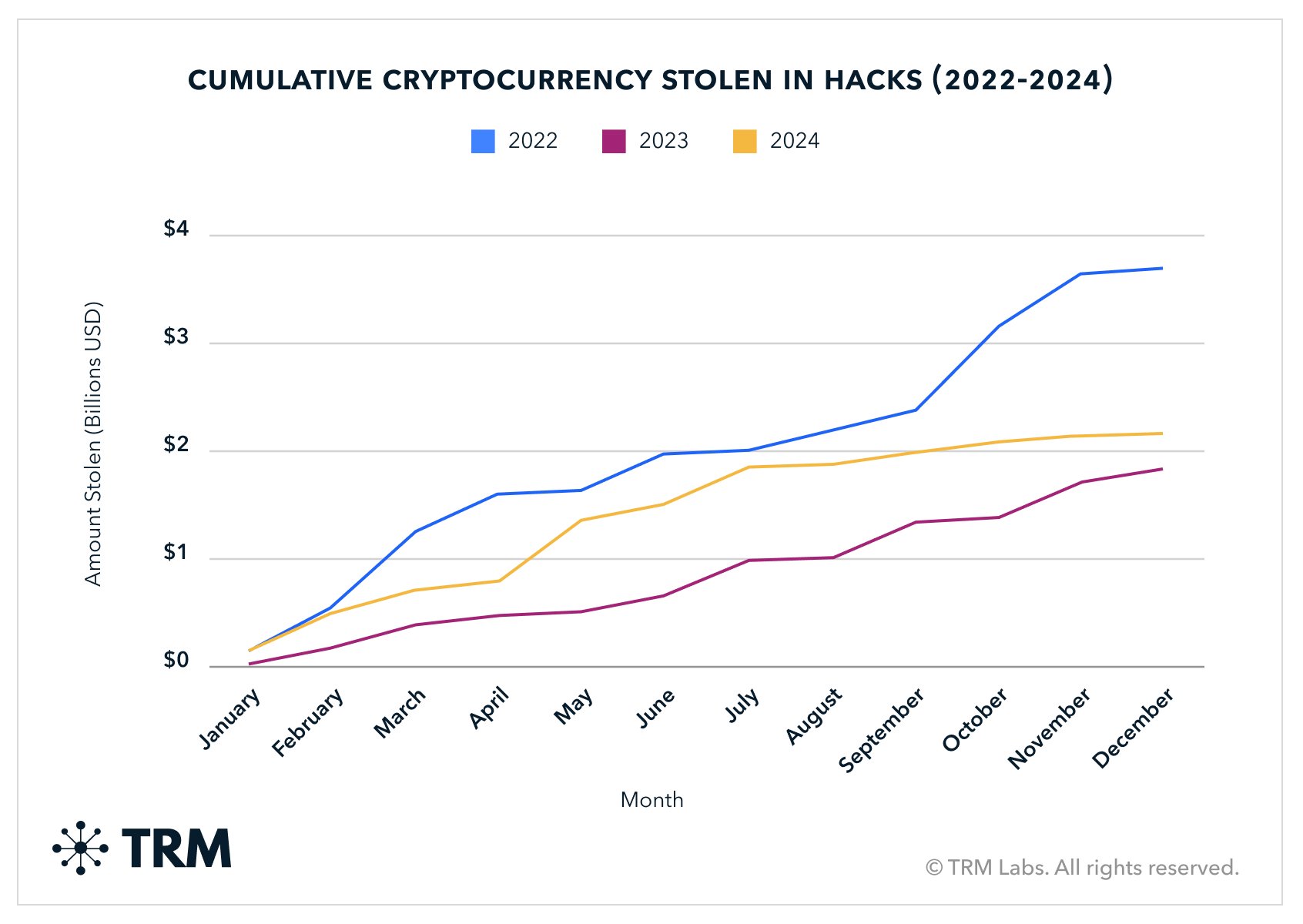

Source: TRM
Lack of Regulatory Clarity and Consumer Protection: DeFi largely operates in an unregulated environment, lacking traditional finance’s extensive oversight. This means fewer legal resources in cases of platform failure or scams. As of early 2025, Europe acknowledges a significant regulatory gap, exposing users to substantial risks.
Scalability Challenges and High Gas Fees: Prominent DeFi networks like Ethereum can face scalability issues and high transaction (“gas”) fees during congestion. While Ethereum’s average fee was around $0.537 in June 2025, spikes can impact smaller investments, a non-issue in traditional bond markets.
Dependence on Crypto Market Volatility: Fixed yield products are tied to underlying crypto asset performance. While the interest rate is fixed, the principal’s value can fluctuate wildly, potentially leading to overall losses in fiat terms. Unlike fiat-denominated traditional fixed income, DeFi assets can experience daily price swings of 5-10% or more.
Current State of the Fixed Yield Market
The DeFi market, including its fixed yield component, shows significant growth and increasing maturity. Total Value Locked (TVL) across all DeFi protocols reached approximately $60 billion by early 2025, peaking over $100 billion in October 2023, signaling growing confidence despite market volatility.
Ethereum still dominates, holding over half of locked value, but Layer 2 (L2) solutions like Arbitrum and Optimism are a major force, collectively holding over $15 billion. This shift reflects users moving to L2s for lower fees and faster transactions, addressing adoption barriers.
Stablecoin yields have dropped from a peak of 16% in late 2021 to a recent average of 3.1%, aligning with global interest rate declines. Despite this, capital flowing into stablecoin deposits on platforms like Aave and Compound has grown substantially from $4 billion to over $15 billion in 12 months. This indicates more resilient capital, driven by DeFi’s transparency and decentralization.
Crucially, institutional participation in DeFi has grown significantly, with a 65% year-over-year increase and over 350 financial institutions now actively engaging. They’re involved in liquidity provision, yield farming, and treasury management, signaling DeFi’s transition from experimental tech to an established financial system component. Cross-chain bridges further boosted interoperability, facilitating over $250 billion in asset transfers in 2023.
Emerging Trends and Future Outlook
The fixed yield DeFi market is characterized by several key emerging trends that will shape its future trajectory:
Real-World Asset (RWA) Tokenization
Real-World Asset (RWA) tokenization is a crucial trend. Indeed, this asset category on DeFi platforms has reached $12 billion. Moreover, it’s growing remarkably at 150% each year. Notably, RWAs include tokenized securities, real estate, and commodities. Credit products also fall into this group.
Consequently, more capital is being allocated to RWAs across different blockchains. This reflects a broader shift. It points to a move towards diversifying yields. It also helps preserve value in traditional capital markets. Ultimately, this trend is pivotal for DeFi. It expands DeFi beyond typical crypto assets. Thereby, illiquid assets gain new liquidity. Fractional ownership becomes possible. Furthermore, RWA integration strengthens the link between traditional finance and DeFi. This lends greater legitimacy to DeFi. As a result, investors can now gain DeFi exposure while still earning traditional yields.
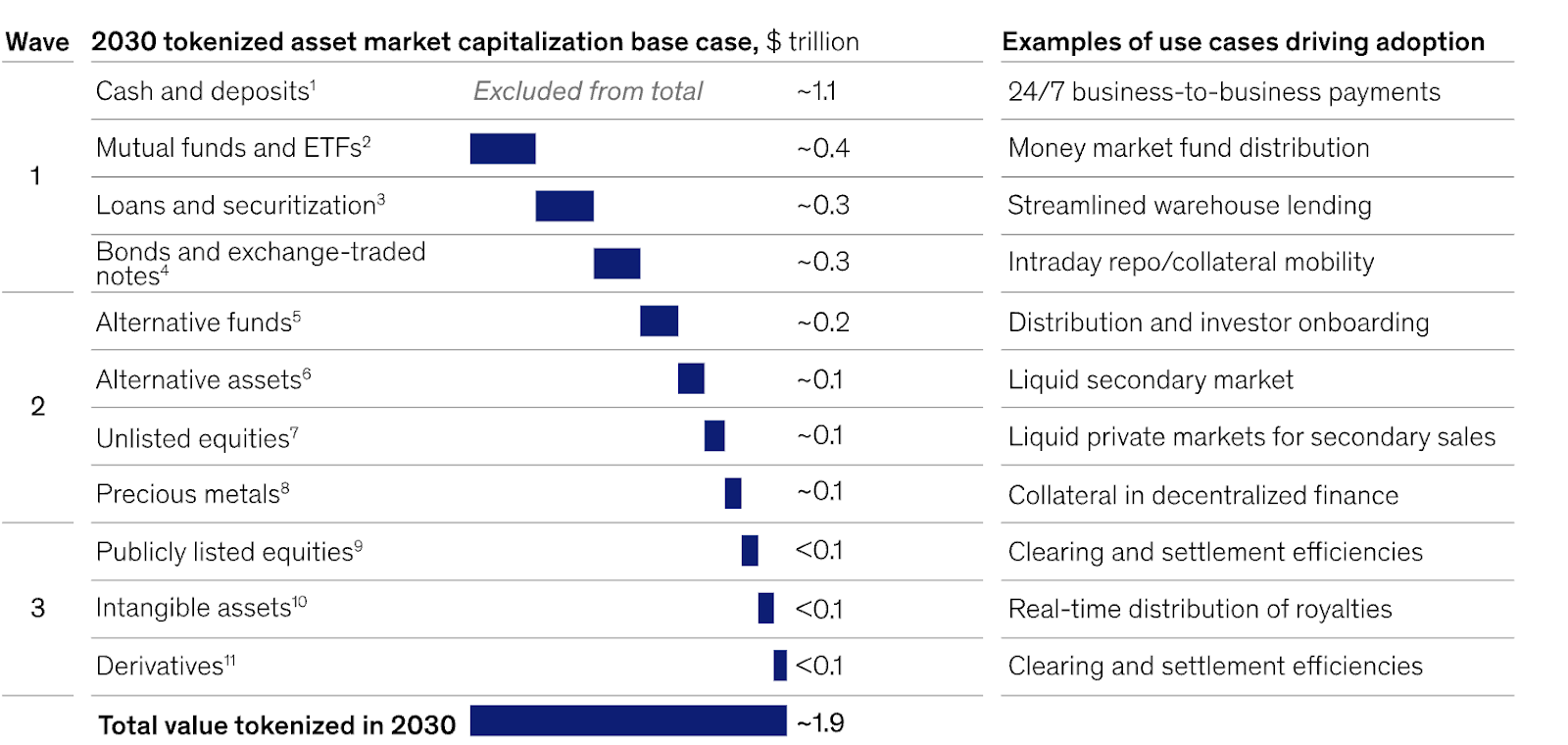

Tokenization waves by asset capitalization
Yield Aggregators and Strategy Protocols
The DeFi landscape is seeing a proliferation of yield aggregators and strategy protocols, such as Yearn Finance. These platforms aim to provide users with auto-optimized, efficient, and sustainable return profiles across various protocols. They serve as an on-ramp for DeFi, simplifying investment for users who may not fully understand the underlying portfolio components. This trend indicates a move towards greater user-friendliness and optimization in yield generation.
Protocol-Owned Liquidity (POL)
Protocols are adopting Protocol-Owned Liquidity (POL) models. This addresses issues from inflationary token emissions. It also tackles “mercenary capital,” which chases temporary yields. Instead of renting liquidity via incentives, protocols build permanent capital bases.
These bases generate sustainable returns. This comes from actual economic activity, not just token inflation. POL makes protocols more resistant to capital flight. This is especially true during market downturns. It also generates consistent fee revenue flowing back to the protocol. This fosters long-term development and security.
Innovation in Yield Generation Models
Beyond traditional borrowing fees and token incentives, newer DeFi platforms are innovating by tapping into alternative yield sources. Examples include funding fees in perpetual markets (where traders in long positions pay fees to short traders) and market-making vaults that earn a share of trading fees and liquidation profits. These models aim to create more market-driven and sustainable yield mechanisms, aligning DeFi yield closer to traditional finance’s structured products or funds.
Regulatory Evolution
As the DeFi sector continues to grow, regulatory frameworks are beginning to take shape. The absence of unified regulations currently creates challenges for DeFi projects, particularly in securing institutional investments and expanding into new markets. However, anticipated regulatory clarity will significantly influence the landscape, potentially fostering greater institutional adoption and market stability.
Scalability Solutions
The continued development and adoption of Layer 2 solutions are crucial for addressing blockchain limitations such as throughput constraints and high transaction costs, particularly on Ethereum. These solutions will enhance the efficiency and accessibility of fixed yield offerings, enabling broader participation.
Conclusions
Fixed yield in DeFi offers predictability and passive income, appealing to diverse investors with stable interest rates. It uses sophisticated mechanisms like fixed-rate lending and tokenized Real-World Assets (RWAs).
However, its “fixed” nature doesn’t remove inherent DeFi risks, including smart contract vulnerabilities, impermanent loss, oracle risks, and governance concerns. Sustainability of yield, especially from inflationary models, remains a challenge being addressed by innovations like Protocol-Owned Liquidity.
Comparing DeFi to traditional finance shows a trade-off: DeFi offers accessibility and innovation, while TradFi provides regulatory clarity and lower inherent risk.
The market shows robust growth, with RWA tokenization being transformative. This trend, alongside yield aggregators and sustainable models, points to a more integrated and mature DeFi future. Investors must understand mechanisms, conduct due diligence, and assess risk tolerance to navigate this evolving landscape.
 Bitcoin
Bitcoin  Ethereum
Ethereum  Tether
Tether  XRP
XRP  USDC
USDC  TRON
TRON  Lido Staked Ether
Lido Staked Ether  Dogecoin
Dogecoin  Figure Heloc
Figure Heloc  Cardano
Cardano  Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin Cash  Wrapped stETH
Wrapped stETH  WhiteBIT Coin
WhiteBIT Coin  Wrapped Bitcoin
Wrapped Bitcoin  Wrapped eETH
Wrapped eETH  USDS
USDS  Chainlink
Chainlink  Binance Bridged USDT (BNB Smart Chain)
Binance Bridged USDT (BNB Smart Chain)  Monero
Monero  LEO Token
LEO Token  WETH
WETH  Stellar
Stellar  Coinbase Wrapped BTC
Coinbase Wrapped BTC  Sui
Sui  Ethena USDe
Ethena USDe  Litecoin
Litecoin  Zcash
Zcash  Avalanche
Avalanche  Hyperliquid
Hyperliquid  Shiba Inu
Shiba Inu  Hedera
Hedera  Canton
Canton  USDT0
USDT0  World Liberty Financial
World Liberty Financial  sUSDS
sUSDS  Dai
Dai  Toncoin
Toncoin  Cronos
Cronos  Ethena Staked USDe
Ethena Staked USDe  PayPal USD
PayPal USD  Uniswap
Uniswap  Polkadot
Polkadot  USD1
USD1  Mantle
Mantle  Rain
Rain  MemeCore
MemeCore  Bittensor
Bittensor  Aave
Aave 


