Staking is now a novel way to earn passive income on idle crypto holdings. The blockchain that uses the proof-of-stake consensus mechanism needs stake contributions to secure the network and validate transactions. By contributing to the network’s stability, users who lock up their tokens for a period get rewarded, and what’s sweeter than “free” money?
However, the biggest drawback of traditional crypto staking methods is that they lock up liquidity. Once a user has locked up their idle crypto, it is no longer accessible for other functions like trading or even DeFi applications. So, what is liquid staking, and what unique solutions does it introduce to users who want to reap more benefits from their idle digital assets?
This comprehensive guide explores this concept of staking, how it works, and its unique benefits. It also introduces some platforms where you can practice this totally new form of staking.
What Is Staking?
Staking is a system within the cryptocurrency space that allows users to earn interest or rewards by investing in holding certain cryptocurrencies. The concept works with cryptocurrencies that use the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, which is one of several consensus models for blockchain networks.
Crypto assets specializing in decentralizing finance (DeFi), like Solana, which uses the PoS protocol, rely on peer-to-peer (P2P) transactions and smart contracts and don’t require traditional banking regulations. There are many benefits associated with staking that could make you consider using your idle cryptocurrency to gain rewards.
When you put money in a savings account at your bank, the institution rewards you with interest rates differing based on your account type. This is similar to staking benefits, where your cryptocurrency can collect rewards identical to the interest you earn at the bank. Staking involves parking your digital assets like Solana, Ethereum, Cardano, and others long-term and receiving rewards for supporting the network’s efficiency, credibility, and security.
What Is Liquid Staking in Crypto?
Liquid staking takes on this challenge head-on as it enables stakers to have liquid assets to cover the place of their staked crypto assets. The liquid staking token, also known as liquid staking derivatives has the same value as the staked token. Users can freely use them for trading, as collateral for crypto loans, or just about any other financial investment function they can employ within the cryptocurrency space. This form of staking is, therefore, an evolution of the native staking system.
Conventional staking involves simply locking idle assets on a PoS blockchain and waiting to earn rewards for contributing to the network’s efficiency and security, making them illiquid. However, liquid staking goes a step further by enabling users to stake their assets while maintaining their liquidity throughout the lockup period. In short, it involves the tokenization of staked cryptocurrencies.
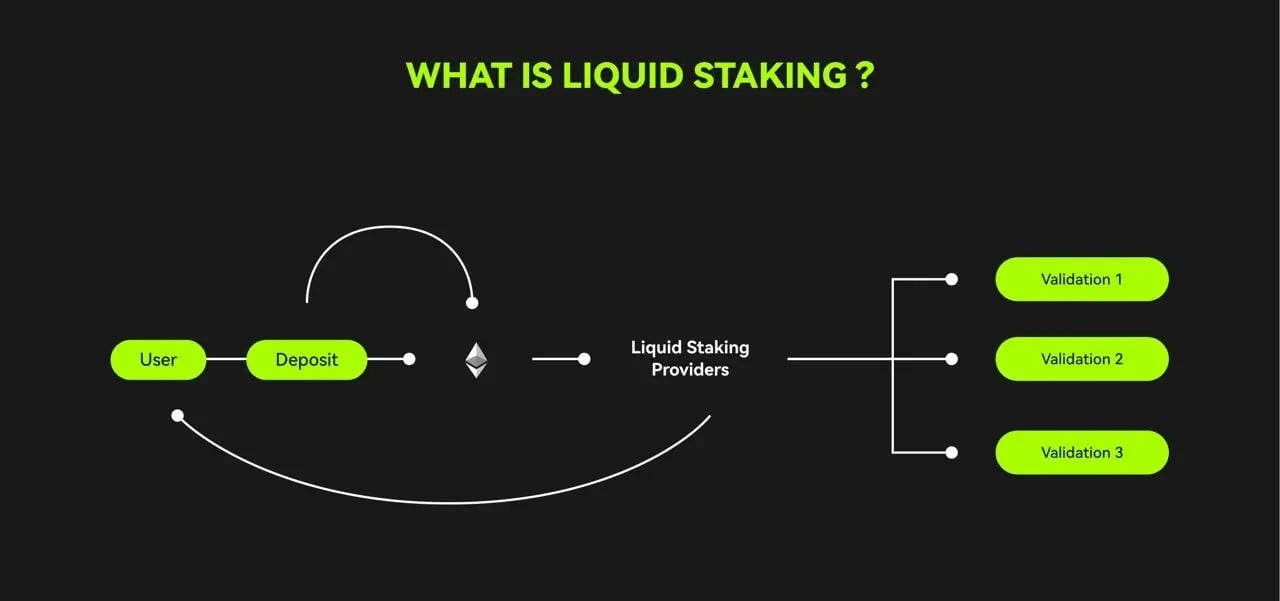

Source: OKX
This new concept offers different mechanisms that enable users to stake their crypto without compromising the liquidity of the staked digital asset. Sometimes, the user receives the Liquid staking token (LST) in return for their staked crypto. For example, when you’re involved in ETH liquid staking on a platform such as Lido, you’re given the stETH token in the staking derivatives model.
Alternatively, you can stake your crypto directly without converting it to an LST in a model known as native staking, such as when you stake ADA on the Cardano blockchain. As a result, staked tokens can have more utility and flexibility as the owners earn extra rewards while maintaining liquidity.
Liquid staking matters because platforms like Cardano, Lido, and others that practice it enable users to receive staking rewards besides giving greater accessibility to their staked coins, which become available for decentralized finance (DeFi) applications. Besides enhancing the overall growth and adoption of crypto by encouraging more active participation, this staking model introduces greater flexibility, enabling users to capitalize more on available investment opportunities and adjust their strategies in line with emerging market conditions.
Liquid staking vs. Traditional Staking: Key Differences
Whether you’re just beginning a staking journey or have some experience, grasping these differences will help you make an informed investment decision.
1. Flexibility
Traditional crypto staking models require users to lock up their tokens completely. Once you have locked your crypto for a predetermined period, you cannot access it until the end. Your tokens are committed to the network’s security, but you are limited in financial flexibility. However, when it comes to the liquid concept, your assets are still available for other uses via a Liquid staking token that you use for DeFi activities.
2. Liquidity
Many investors are genuinely concerned about liquidity, which the regular staking doesn’t provide since staked assets are locked in. This can be a disadvantage when you need access to your funds to respond to market changes. On the other hand, with the liquid model, you still have access to your funds because Liquid staking derivatives enable you to leverage your staked crypto in other financial activities, making them more appealing.
3. Risk
Native staking exposes you to great risks, such as those inherent in your selected blockchain, including network security or validator downtime issues. Besides the greater flexibility you enjoy with liquid staking, you become vulnerable to extra risks associated with the staking protocol, such as smart contract weaknesses or counterparty risk related to the platform running the staking program.
4. Rewards
When seeking rewards in the regular staking program, the matter is consistent and straightforward, but you could miss out on emerging opportunities because your hands are tied. On the other hand, the liquid model may initially offer lower rewards because of the cut taken by the liquid staking protocol. Nonetheless, you can use the LSTs you receive in DeFi activities to offset the difference.
What Are Liquidity Pools in Crypto?
Liquidity pools in crypto refer to a collection of digital assets and tokens locked up in a smart contract. They build the foundation for DeFi activities like lending, trading, and other financial activities where traditional intermediaries are eliminated. Liquidity pools in DeFi facilitate 24/7 opportunities for users to earn passive income by providing liquidity. While they may look simple, Liquidity pools are the powerhouse that moves complex financial interactions on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and DeFi platforms.
Users who contribute pairs of tokens to the pool are called liquidity providers, and their funds move the lending protocols and DeFi NFT projects. As a reward for their contribution, Liquidity providers earn a percentage of the trading fees the pool generates, while others offer governance tokens and yield farming opportunities as extra incentives. When users want to conduct business, they can approach a liquidity pool instead of traditional order books.
Why Are Liquid Staking Tokens (LSTs) Gaining Popularity?
Liquid staking tokens (LSTs) are becoming more popular by the day as they combine the benefits associated with staking and the liquidity of traditional assets. As a result, investors can access their assets for trading, lending, and other DeFi activities while also earning staking rewards. Among the tangible benefits associated with LSTs that make them popular include:
- Increased Liquidity and Flexibility: Where traditional staking locks up assets for the entire lockup period, LSTs offer a tokenized representation of the user’s staked cryptocurrency, enabling them to trade, transfer, and use them in DeFi platforms.
- Capital Efficiency: With LSTs, users can simultaneously earn staking rewards while using the same staked crypto for DeFi yield farming, lending, and borrowing activities, creating capital efficiency that maximizes returns.
- Lower Barriers to Entry: Compared to traditional staking platforms that require a minimum of 32 ETH to run a validator note, some LSTs like Rocket Pool and Lido Finance enable users with smaller ETH amounts to join the pools.
- Access to DeFi Opportunities: Investors can use LSTs as collateral in lending platforms, trade them in DEXs, and provide liquidity in AMMs, enabling users to expand their portfolio strategies.
- Cross-Chain Capabilities: Investors can use LSTs across different blockchains, enabling them to easily leverage DeFi opportunities and staking benefits across different blockchains.
- Enhanced Yield Opportunities: LSTs combine DeFi activities and staking rewards, potentially bringing a higher return on investment than normal staking.
Liquid Staking vs. Pool Staking: What’s the Difference?
Pooled staking or pool staking refers to a method that allows users to combine their staking resources in crypto staking. As a result, users who pool their resources can benefit individually and collectively without employing too many resources upfront. Once the rewards have been paid, they’re shared within the pool relative to every participant’s contribution. The method can especially benefit users who want to benefit from staking but lack the resources to do it independently.
Pool staking and liquid staking could be similar in many aspects, but there are still a few similarities and differences that you may want to consider before you can choose between the two:
1. Liquid Staking
Liquid stakers receive Liquid staking derivatives like mSOL and stETH depending on the asset they staked. They can use these assets for different DeFi activities while simultaneously earning rewards. The tokens become their bond, indicating that what they have staked maintains its utility value and liquidity.
2. Pool Staking
Investors who participate in pool staking combine their resources to achieve the minimum quota required by a platform to achieve a validator node status. The pooled assets are then frozen and remain untouched throughout the lockup period. This enables users with smaller amounts of disposable assets to participate in staking without committing too many resources.
When it comes to the key differences between the staking model under consideration and pool staking, you want to remember the following:
- Flexibility: You can use your Liquidity staked tokens for other purposes, like trading, lending, and yield farming, which isn’t achievable with locked staking pools.
- Liquidity: Funds in staking pools are locked entirely, while liquid stakers are assured of liquidity through LSTs.
- Risk Profile: Staking pools focus on network risks such as slashing, while Liquid stakers have to deal with issues like smart contract vulnerabilities.
Due to its potential benefits, Liquid stakers have made it emerge as a more preferred option compared to other forms of staking due to their limitations. LSTs introduce greater flexibility and a higher ROI. Consider your individual circumstances, investment goals, and available resources when choosing between native staking, pool staking, and liquid staking.
How Does Liquid Staking Work?
Liquid staking begins with issuing Liquid staking derivatives representing the staked cryptocurrencies. The user needs to visit a liquid staking protocol to receive derivative tokens representing the value of their staked cryptocurrencies.
The investor can use the derivative tokens in different DeFi activities while their original digital asset remains locked in the traditional staking process. The user receives a double reward from the staked crypto assets and income from investing in the derivative tokens.
The following is a step-by-step guide for getting started:
- Step 1: Deposit: The investor deposits a token like Ethereum (ETH) or Solana (SOL) into a Liquid staking protocol.
- Step 2: Token Minting: The platform mints the LST in a ratio of 1:1 to the deposited cryptocurrency so that, for example, staked ETH yields stETH tokens.
- Step 3: Staking: The platform stakes the deposited assets on behalf of the user by distributing them across different validators on PoS networks to mitigate risk.
- Step 4: Reward Accrual: As staking rewards accumulate, the user revives the derivative token representing their staled assets to use in trading, lending, or any other DeFi activity. In the meantime, the accumulated rewards are reflected in the value of LSTs.
- Step 5: Unstaking: If the investor wishes to retrieve their original staked assets, they return “burn” their staking tokens to withdraw the equivalent amount of the staked token and the accrued rewards.
By following this simple mechanism, investors can maximize the utility of their idle crypto assets while maintaining their liquidity. By tokening their staked cryptocurrencies, they earn passive income. They can also explore the broader DeFi ecosystem, bridging the gap between securing PoS networks and becoming part of the DeFi space.
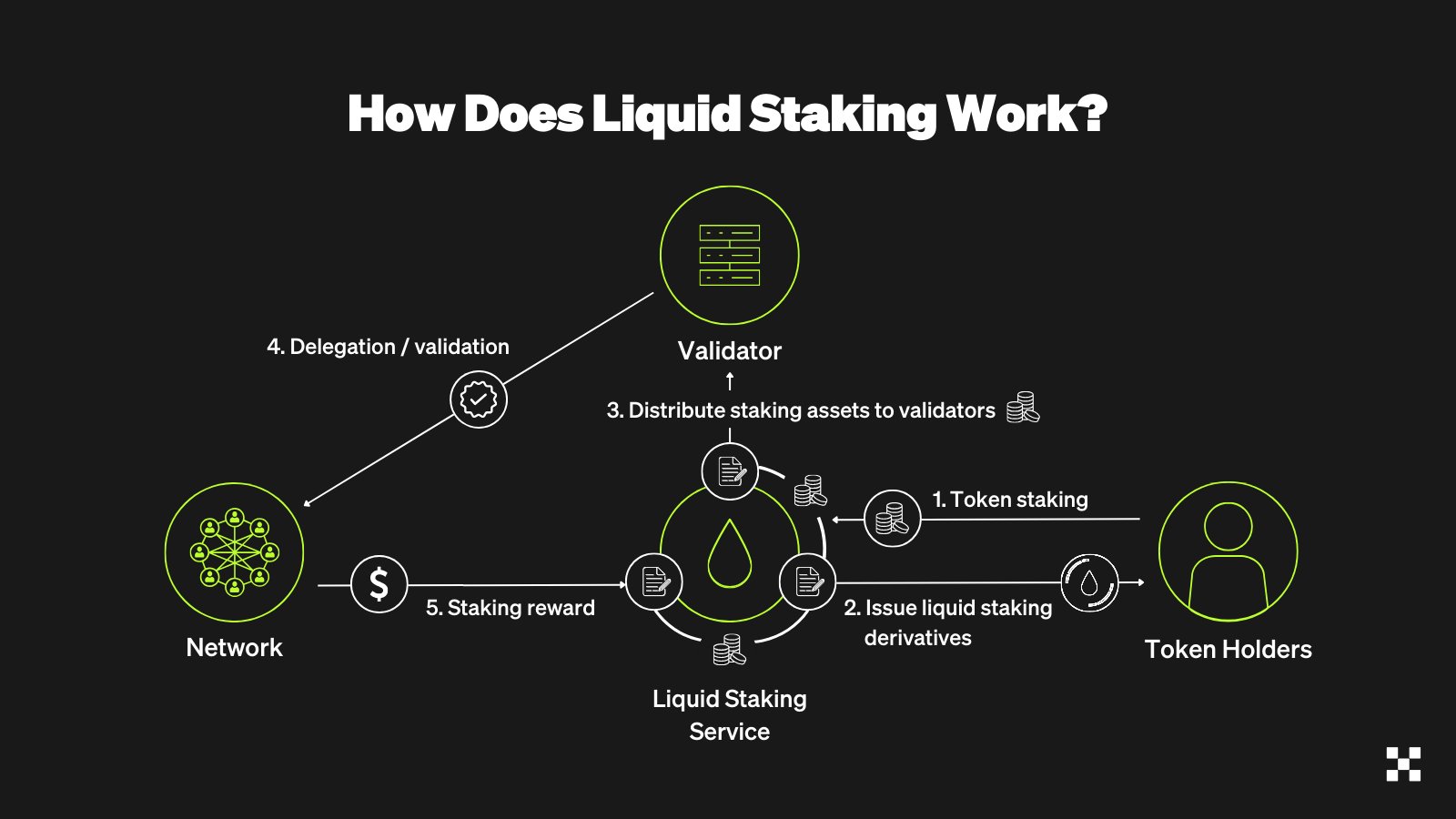

Source: OKX
Some of the most critical aspects of the staking process that you need to keep in mind include the following:
Validators
Validators play a critical role in the entire staking process by guaranteeing the security and operations in a Proof-of-Stake blockchain. Liquid staking protocols partner with expert node operators to maintain the security of staked assets.
Consensus Mechanisms
Staking platforms use the PoS consensus mechanism where chosen validators remain vigilant to ensure the network remains decentralized and tamper-proof.
Liquid Staking Tokens (LSTs)
LSTs represent the value of your staked crypto assets, and users can employ them in different trading or lending activities on DeFi platforms and decentralized exchanges.
Liquid Staking Derivatives (LSDs)
These are advanced tokens in the staking ecosystem, representing fractional ownership of the staked rewards, which offers even more flexibility for experienced investors.
What Is Restaking?
Restaking within the crypto space refers to using staked assets to secure multiple protocols to enhance capital efficiency and generate additional rewards. The process leverages already staked digital assets in new ways, making an investor’s funds bring in a greater ROI. This is achieved through:
- Capital Efficiency: By allowing users to use their staked crypto for multiple purposes instead of having them locked in a staking pool, restaking enhances the funds’ potential to generate extra income.
- Additional Rewards: When users retake their assets, they receive rewards beyond the traditional staking rewards, thereby incentivizing participation and cryptocurrency adoption.
- Liquid Restaking: Some platforms allow liquid restaking, allowing stakers to receive tokens representing their assets, which they can use for DeFi activities to generate more rewards.
Benefits of Liquid Staking
There are many compelling benefits associated with the new staking model that transcend the traditional staking method. Besides giving you greater control over your idle crypto assets while you still enjoy earning staking rewards, the following are other advantages worth considering:
1. Unlocked Liquidity
With the liquid model of skating, you don’t simply lock away your tokens for a set period and wait idly. You enjoy your cryptocurrency’s liquidity by receiving LSTs, tradable assets you can invest in by buying, selling, or using as collateral in DEXs and DeFi platforms to generate additional yield.
2. Many DeFi Protocols
The staking concept supports platform interoperability, meaning you can interact with DeFi platforms across blockchain networks. As a result, you can enjoy seamless staking and other DeFi services, thus unlocking fresh opportunities for financial innovation and additional income.
3. Staking Rewards
You will still enjoy passive income generated via proof-of-stake blockchain. The staking pool you join will share a portion of the rewards they earn with you based on your LSTs shareholding.
4. Avoid Complex Infrastructure
The flexibility that comes with the Liquid model helps you manage your staked digital assets more effectively so that you don’t need to choose between one since both can be executed simultaneously. As a result, you earn income from more than one stream without moving your funds from one platform to another, which is especially important in volatile markets or when you need to access your capital immediately.
Risks and Limitations of Liquid Staking
Similar to all other investment opportunities, especially with new asset classes, there is always some risk associated with this form of staking. While all staking activities are legitimate, you should expect to encounter the following limitations:
1. Slashing
Just like traditional staking, the staking concept also carries the possibility of slashing. This refers to situations when a validator becomes negligent or malicious, leading to penalties that reduce your staked assets. Suppose staked assets are liquidated and used actively for another purpose. In that case, you may not have sufficient control over your staking position, which increases the potential of an unintentional action that could result in a slashing penalty. The solution to this problem lies in choosing a reliable validator to mitigate risk.
2. Exploits
Liquid staking protocols use third-party platforms to convert staked assets into LSSTs, introducing counterparty risk since unreliable parties could easily exploit the situation. Once again, care must be taken when choosing service providers since a compromised third-party platform or one that experiences technical issues could lead to potential losses.
3. Yield Volatility
This new form of staking exposes investors to volatility inherent in the digital asset market. Even with the benefits associated with the flexibility that this new form of staking introduces, users must be aware that they are still subject to greater market fluctuations compared to having left their assets locked quietly in traditional skating. You could easily experience losses when the value of a liquid token decreases significantly.
Top Liquid Staking Protocols
As this advanced staking model continues to gain popularity, the number of platforms attracting users interested in participating is increasing. Below is our exclusive list of the best Liquid staking platforms you could consider looking at:
1. Lido

Lido Finance offers a centralized staking service that supports assets like Ethereum, Solana, and Polygon, which are converted to tokens like stETH and stSOL. The platform is the leading staking platform, with data showing it has over $14 billion in total value locked (TVL)
Investors interested in liquid ETH staking on Lido have the platform aggregate their deposits, and in return, they receive stETH representing their stake in the pool. The stETH they receive is a tradable asset that enables the investor to maintain liquidity for their staked ETH.
2. Rocket Pool

Rocket Pool also specializes in ETH liquid staking, where investors can stake their ETH and receive rETH tokens in return. The platform runs a decentralized staking model where users can become mode operators if they lock up ETH and RPL, the platform’s native token. On the other hand, investors can become stakers by depositing their ETH and waiting to earn rewards without running staking nodes so that, in return, they receive rETH, the platform’s staking token.
How Does Liquid Staking Work With Different Cryptocurrencies?
While the functionality remains the same, the new staking process could differ across blockchain networks in practice. To better understand this, we shall consider how it works with among the leader cryptocurrencies:
1. Ethereum


Source: Messari
Platforms that support Ethereum liquid staking mostly create stETH, which tracks the investor’s staked ETH. Apart from the regular staking rewards, the user will have the token enabling them to participate in other activities within the DeFi ecosystem using the LST, which is stETH. Here’s how liquid staking works with Ethereum:
- Stake ETH: The user deposits ETH in the liquid staking protocol
- Receive LST: The investor receives an LST like stETH (Lido) or mSOL (Rocket Pool) in place of their staked ETH
- Use the LST: Investors can use the LST to participate in different activities such as collateral for loans, trade on an exchange, or deploy in other DeFi activities. Alternatively they can deposit the LST into yield farming or trade in an exchange like other crypto assets.
2. Solana
Users interested in Solana staking will receive mSOL, an LST. They can use liquid pools and lending platforms to allow investors to earn rewards from their tokens while maintaining their liquidity. The mSOL token they receive is a derivative token representing the value of their staked SOL, which can be used in DeFi applications or traded. The process is also easy to follow:
- Stake with SOL: Stake your SOL for a chance to earn rewards either by delegating to a validator or directly through a liquid staking protocol.
- Liquid Staking Pools: The platforms stake your SOL indirectly via staking pools or smart contracts. The pol delegates your staked SOL to a validator.
- Receive LSTs: After you deposit SOL, you will receive an LST like mSOL or stSOL, which represents the value of your staked SOL, which continues to earn rewards.
3. Polygon and Others
Other chains like Polygon also implement staking to attract more user activity and let users participate in staking. Rather than facilitating the traditional staking program, they allow liquid staking using derivative tokens (like ankrPOL or stETH) representing the staked crypto assets they can trade or use as collateral in DeFi platforms.
Stake POL tokens: Deposit POL and receive an LST, AnkrPOL, representing the value of your staked asset. You can use the LST in different DeFi activities, including trading, lending, and borrowing.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Liquid Staking
Big centralized cryptocurrency exchanges like Binance and Coinbase support staking, where users allow the platform to act as a custodian and staking operator on their behalf. Some users prefer the centralized liquid staking option because of its convenience, especially beginners who may not yet have the technical skills required. However, the most significant challenge with centralized liquid staking is that it exposes users to the usual counterparty risks, such as mismanagement, insolvency, or regulatory difficulties often associated with centralized platforms.
On the other hand, decentralized staking protocols like Rocket Pool and Lido Finance don’t have a single point of failure. These platforms give users sovereignty over their crypto assets as they don’t depend on any centralized intermediary. Nonetheless, for a user to participate conveniently, they need to acquire some skills associated with W3b3 platforms and be familiar with DEXs and smart contracts. A user must also account for network congestion, gas fees, and smart contract risks as they execute decentralized staking.
Conclusion
As DeFi continues to develop, liquid staking could play an integral role in bridging the gap that has always existed between staking and liquidity provision for the investor. The flexible alternative it introduces has the potential to alter how investors interact with the DeFi application and the proof-of-stake consensus mechanism. It is also improving blockchain security measures, which could lead to better integration within the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem. Cross-chain staling interoperability now enables stakers to use assets from one blockchain and utilize their derivative tokens in another, further promoting blockchain interoperability.
Remember that if you have a lower risk tolerance and prefer to lock up your assets, traditional staking is for you. However, if you wish to maximize returns associated with your staked assets and you want to access your funds for other DeFi applications, liquid staking is your cup of tea.
FAQs
Is liquid staking worth it?
Liquid staking is often considered a worthwhile strategy, as it allows users to earn staking rewards while still maintaining access to their assets. This flexibility makes it attractive to those who want to maximize yield without sacrificing liquidity.
What are the risks of liquid staking?
There are several risks associated with liquid staking, such as risks associated with smart contracts, potentially higher fees relative to traditional staking, and market volatility since the value of liquidity tokens (LSTs) can fluctuate. Other risks include de-pegging LSTs from the underlying asset, potential impermanent loss, and existing regulatory uncertainties.
Is liquid staking a taxable event?
Liquid staking is considered a taxable event, especially since the conversion of staked tokens such as ETH to STETH results in rewards that are generally subject to tax.
What is Ethereum liquid staking?
Ethereum liquid staking refers to investors participating in ETH staking to secure blockchain networks and earn rewards while maintaining the liquidity of their staked cryptocurrencies. Rather than wait for the traditional unstaking practice, liquid staking protocols offer users tokens representing their staked ETH to use in various ways.
What is the difference between liquid staking and lending?
Liquid staking and lending are entirely different but related activities within the cryptocurrency space. While lending involves loaning out funds to borrowers and receiving interest, liquid staking enables users to stake their crypto assets and continue earning rewards via tokenized assets. Lending facilitates borrowing, while liquid staking focuses on securing PoS networks.
 Bitcoin
Bitcoin  Ethereum
Ethereum  Tether
Tether  XRP
XRP  USDC
USDC  TRON
TRON  Lido Staked Ether
Lido Staked Ether  Dogecoin
Dogecoin  Figure Heloc
Figure Heloc  Cardano
Cardano  Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin Cash  Wrapped stETH
Wrapped stETH  WhiteBIT Coin
WhiteBIT Coin  Wrapped Bitcoin
Wrapped Bitcoin  USDS
USDS  Wrapped eETH
Wrapped eETH  Chainlink
Chainlink  Binance Bridged USDT (BNB Smart Chain)
Binance Bridged USDT (BNB Smart Chain)  Monero
Monero  LEO Token
LEO Token  WETH
WETH  Stellar
Stellar  Zcash
Zcash  Coinbase Wrapped BTC
Coinbase Wrapped BTC  Sui
Sui  Ethena USDe
Ethena USDe  Litecoin
Litecoin  Hyperliquid
Hyperliquid  Avalanche
Avalanche  Shiba Inu
Shiba Inu  Hedera
Hedera  Canton
Canton  sUSDS
sUSDS  USDT0
USDT0  World Liberty Financial
World Liberty Financial  Toncoin
Toncoin  Dai
Dai  Cronos
Cronos  PayPal USD
PayPal USD  Ethena Staked USDe
Ethena Staked USDe  Uniswap
Uniswap  USD1
USD1  Polkadot
Polkadot  Mantle
Mantle  Rain
Rain  MemeCore
MemeCore  Bittensor
Bittensor  Pepe
Pepe 


